




































































































































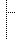




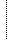
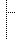


















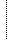
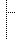




































































Figure 4.1: Road Information Tree Structure

|


|



|



|



|



|


|



|




|


|



|



|



|



|



|



|



|



|



|



|


|



|




|




|



|



|

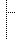
|

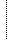
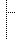
|



|


|



|




|




|



|



|



|



|



|


|


|



|




|




|



|



|



|

|



|

|



|


|



|



|



|



|

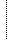
|



|



|


|



|




|




|



|



|



|



|



|


|



|



|



|



|



|


|



|



|



|



|



|
Figure 4.1: Road Information Tree Structure |
This section contains basic information regarding roads.
This section lists the elements that make up basic information. Base individual elements on 3. Basic Information Structure.
This section contains information related to road weather.
This section contains information for road weather in observed locations.
This section contains information for observed points.
<observe-point>
<latitude>Latitude</latitude>
<longitude>Longitude</longitude>
<altitude>Altitude</altitude>
<point-name>Point Name</point-name>
<observe-code system>Enter Observation Code Here</observe-code>
</observe-point>
When an observation code is attached to a code for a given system, the code designates that system.
All other cases follow the notation rules in 3.1.1 Point.
<observe-point> <latitude>41,500000</latitude> <longitude>142,250000</longitude> <altitude>15.3</altitude> <point-name>Nakayama Toge</point-name> <observe-code system="weather ">9999</observe-code> </observe-point>
This section gives information for observed routes.
<observe-route>
<route-name>Route Name</route-name>
<road-class>Road Class</road-class>
<toll>Toll</toll>
<route-position>Route Position</route-position>
<Observation Code System >Observation Code</observe-code>
</observe-route>
Refer to the notation rules in 4.2.1.1 for Observation Code and 3.1.2 Route for other items.
<observe-route> <route-name>Sasson Expressway</route-name> <route-position>Otaru IC</route-position> <observe-code system="WEATHER">A999</observe-code> </observe-route>
This section gives the date and time of observation.
Refer to the date and time notation rules in 2.2.1 Date and Time.
<observe-time>Observation Date and Time</observe-time>
<observe-time>1999-04-01T16:30+09:00</observe-time>
This section contains the weather status.
<weather type="Pattern">Weather</weather>
Numeric codes and characters are listed below. If there is no designation for attribute type, notate by characters only.
Code Characters 1 Clear 2 Fine 3 Slightly Cloudy 4 Cloudy 5 Hazy 6 Dust Storm 7 Drifting Snow 8 Fog 9 Drizzle 10 Rain 11 Sleet 12 Snow 13 Graupel 14 Hail 15 Lightning
| Attribute Name | Attribute Value | Value Upon Omission | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| type | code, text | text | Input numeric code or characters. |
<weather type="text">Excellent Conditions</weather>
This section contains atmospheric temperature information.
<temperature>Temperature </temperature>
Temperature is expressed in Celsius. Notations extend out to the first decimal place. When the temperature is below zero degrees Celsius, a [-] minus mark is placed before the number representing the temperature. The decimal value can be omitted.
<temperature>-2.1</temperature>
This section gives the relative atmospheric humidity.
<humidity>Humidity</humidity>
Humidity is measured in terms of "relative humidity". It is expressed in percentage. The decimal value is omitted.
<humidity>70</humidity>
This section notes which direction the wind is blowing from.
<wind-direction code="Code">Enter Wind Direction Here</wind-direction>
Notation for wind direction is given below in numeric code and alphabetic code. With true north serving as a standard, wind direction is expressed by dividing a circle clockwise into 16 sections. Use the attribute code to specify whether alphabetic code notation or numeric code notation is used. If there is nothing written in the attribute code, it is understood that alphabetic code is being used to designate wind direction. When the wind speed is under 0.2 m/s, this is regarded as no wind and "calm" is entered. The numeric code "00" and the alphabetic code "C" is used for "calm".
Direction Numeric Code Alphabetic Code North 16 N North North East 01 NNE North East 02 NE East North East 03 ENE East 04 E East South East 05 ESE South East 06 SE South South East 07 SSE South 08 S South South West 09 SSW South West 10 SW West South West 11 WSW West 12 W West North West 13 WNW North West 14 NW North North West 15 NNW Calm 00 C
| Attribute Name | Attribute Value | Value Upon Omission | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| code | num, alpha | alpha | Specify whether a numeric code or alphabetic code. |
<wind-direction>NNE</wind-direction> or <wind-direction code="num">01</wind-direction>
This section gives the distance that air moves in unit of time.
<wind-speed>Wind Speed</wind-speed>
Wind speed is expressed in m/s. The wind speed value is recorded up to 1/10 m/s. When wind speed is at or below 0.2 m/s, it is recorded as 0.
<wind-speed>3.6</wind-speed>
This section gives the visibility distance (the farthest distance that can be measured by eyesight).
<visibility>Visibility</visibility>
Visibility is expressed in the unit "m". Visibility can extend up to 100 m under good conditions. When visibility exceeds 1000 m, "excellent" can be recorded.
<visibility>500</visibility>
This section gives the amount of precipitation that reached the earth surface in unit of time.
<precipitation span="Unit of Time">Precipitation Amount</precipitation>
Precipitation is expressed in the unit "mm". Precipitation value is recorded up to 1/10 mm. Regarding observation decimal values, decimal values less than 0.5 are rounded down to 0. Values ranging from equal or greater than 0.5 to less than 1.0 are rounded to 0.5.
In the case that, due to obstacles, observation data can not be obtained, specify this by recording "nodata". In this case, clearly indicate time by using attribute span as the unit of time.
When the attribute span is omitted, it is understood that the value recorded is for a period of one hour starting one hour before time observed.
| Attribute Name | Attribute Value | Value Upon Omission | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| span | hourly, pre03, pre06, pre12, pre24, daily | hourly | Hourly precipitation amount 3 hours previous precipitation amount 6 hours previous precipitation amount 12 hours previous precipitation amount 24 hours previous precipitation amount Daily precipitation amount |
<precipitation>8</precipitation> or <precipitation span="pre24">25</precipitation>
This section indicates the depth of fallen snow that naturally piles up and covers the ground.
<snow-depth measure="Observation">Snow Depth</snow-depth>
The current snow depth is expressed in units of "cm". In the observation process, clarify whether the observation means is visual observation (manual) or snowdepth meter (auto) using the attribute measure. When the choice of method is not clarified, the value is assumed to be from the snowdepth meter (auto).
| Attribute Name | Attribute Value | Value Upon Omission | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| measure | manual, auto | auto | Indicate visual observation (manual) or snowdepth meter observation (auto). |
<snow-depth measure="manual">123</snow-depth>
This section indicates the depth of snow that is piled on the ground within a given amount time.
<snow-fall span="Observation Target Period" measure="Observation">Fallen Snow Depth</snow-fall>
For the depth of fallen snow, the amount of snow that falls within the observation target time period is expressed in "cm" units. The measurement target time period must be clarified in the attribute span. As a rule, the attribute span is expressed following the notation style in 2.2.4 Time Length and Period. However, for the following specific time periods, it is acceptable to use the attribute values given below (hourly, daily 21, daily 09) to
In the observation process, clarify whether the observation means is visual observation (manual) or snowdepth meter (auto) using the attribute measure. When the choice of method is not clarified, the value is assumed to be from the snowdepth meter (auto).
| Attribute Name | Attribute Value | Value Upon Omission | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| span | CDATA, hourly, daily21, daily09 | #REQUIRED | List the commencement time and the conclusion time as seen in 2.2.4 Time Length and Period. Value at 1 hour previous (hourly), Daily Snowfall Amount: 21:00 (daily 21), Daily Snowfall Amount: 09:00 (daily 09) |
| measure | manual, auto | auto | Indicate visual observation (manual) or snowdepth meter observation (auto). |
<snow-fall span="daily21" measure="manual">15</snow-fall> or, <snow-fall span="hourly">3</snow-fall> or, <snow-fall span="T09/T15" measure="manual">8</snow-fall>
This section gives information relating to the condition of the road surface.
This section indicates the location of the road surface that is observed.
This section indicates the date and time of road surface observation.
Follow 4.2.2
This section indicates the road surface slipperiness classification.
<surface type="Pattern">Road Surface Condition</surface>
Express using the road surface condition classification code. Use the simple classification system below (7 distinctions).
Regulate the use of code or description coresponding to the attribute type.
Code Road Condition 1 Very slippery road surface 2 Icy road 3 Compacted Snow 4 Powder snow / Granular snow 5 Slash 6 Wet 7 Dry
| Attribute Name | Attribute Value | Value Upon Omission | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| type | code, text | text | Indicate code or description |
<surface>Sherbet</surface>
This section describes the slipperiness of the road surface in detail.
<surface-detail type="Pattern">Road Surface Condition in Detail</surface-detail>
The road surface condition is expressed with the road surface condition classification code. For classification, the road surface classification system from Hokkaido Development Bureau winter period road surface management manual (13 classifications) is used.
Regulate the use of code or characters coresponding to the attribute type.
Code Road Surface Condition in Detail 11 Very slippery ice film 12 Very slippery ice crust 13 very slippery compacted snow 14 Ice crust 15 Powder snow on ice-plate layer 16 Ice film 17 Granular snow on ice crust 18 Compacted snow 19 Powdey snow 20 Granular snow 21 Sherbet 22 Moist 23 Dry
| Attribute Name | Attribute Value | Value Upon Omission | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| type | code, text | text | Indicate code or characters. |
<surface-detail type="code">13</surface-detail>
This section indicates the temperature of the road surface.
<surface-temperature>Road Temperature</surface-temperature>
Road tempurature is expressed in celsius and the value is extended to 1/10 of a degree. When the temperature is below 0 degrees, a [-] (minus mark) is attached before the number. In this case, the decimal value can be omitted.
<surface-temperature>-0.2</surface-temperature>
This section indicates the salinity content rate of water on the road surface.
<surface-salt>Road Surface Salt Content</surface-salt>
Road surface salt density is expressed in percent. Value is extended to 1/10 of a percent.
<surface-salt>9.8</surface-salt>
This section gives information relating to images gathered from taking pictures of the road.
This section gives information for the location where the camera images were taken.
Follow 4.2.1
This section indicates the date and time for which the camera images were taken.
Follow 4.2.2
This section indicates camera image file names.
<image-file src="URL">Image Title</image-file>
Camera images are given a file name. Follow URL notation for the method of specifying a file name.
| Attribute Name | Attribute Value@ | Value Upon Omission | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| src | CDATA | #REQUIRED | Specify an image file location. |
<image-file src="www.rwmlserver.ne.jp/images/img99990507.jpg">1999-05-07 Camera Image</image-file>
This section indicates the camera data.
<camera>Camera Data</camera>
Camera data is expressed in characters. Abbreviations are permitted. Specify each image file.
<camera>Camera No.0103, Camera Height 7m, 35mm Wide Angle Lens</camera>
This section gives a supplementary explanation for images.
<comment>Image Explanation</comment>
Comments regarding camera images are expressed in characters. Each image file is specified.
<comment>Image Taken at Nakayama Toge in the Direction of Sapporo</comment>
This section gives information obtained from processing the camera images
<image-process>Image Processing Information</image-process>
Observations which originate from the use of camera and are obtained from camera images are expressed in characters. Each image file is specified.
<image-process>Accident Occurence </image-process>
This section indicates the movability condition of equipment.
<equipment-condition>Equipment Condition</equipment-condition>
Equipment movablity condition is expressed in characters. No code is used for notation. Each image file is specified.
<equipment-condition>Trouble: File Error</equipment-condition>
This section gives information related to congestion.
This section indicates the target location for congestion.
Follow 4.2.1
This section indicates the date and time presented for congestion.
Follow 4.2.2
This section indicates the status of congestion.
<congestion-status>Congestion Status</congestion-status>
The degree of the congestion can be classified into traffic jam, crowding, or natural flow. It is not a requirement to utilize these classifications.
<congestion-status>Congestion</congestion-status>
This section gives the congestion top location.
<congestion-top>
<point>
<latitude>Latitude</latitude>
<longitude>Longitude</longitude>
<altitude>Altitude</altitude>
<point-name>Point Name</point-name>
</point>
<route>
<route-name>Route Name</route-name>
<route-position>Route Position</route-position>
</route>
</congestion-top>
For point, route name, and route position, refer to the notation style in 3.1 Place.
Information that is included in the observation place section can be omitted.
<congestion-top>
<point>
<latitude>38,500000</latitude>
<longitude>137,250000</longitude>
<altitude>103</altitude>
<point-name style="poplular">Tunnel #1</point-name>
</point>
</congestion-top>
This section gives information relating to downstream congestion flow or the congestion direction.
<congestion-direction>Congestion Direction</congestion-direction>
Congestion direction is expressed in characters.
<congestion-direction>Outer Lane</congestion-direction>
This section gives the length of the congested area.
<congestion-length>Congestion Length</congestion-length>
Congestion length is expressed in km units. Value is extended to 1/10 km.
<congestion-length>3.5</congestion-length>
This section gives the congestion outbreak time.
<outbreak-time>Congestion Outbreak Time</outbreak-time>
If the congestion begins due to a time specifiable phenomenon, note the time. Refer to the notation style in 2.2.1 Date and Time.
<outbreak-time>1999-10-01T17:15</outbreak-time>
This section explains the cause of the congestion.
<congestion-cause>Congestion Outbreak Cause</congestion-cause>
Note the cause of the congestion. If the nature of the congestion necessitates the use of notation that does not coincide with the regulated notation style, it is possible to use characters for notation.
(1) Natural Congestion (2) Traffic Jam (3) Congestion caused by sightseeing or inattentive driving (4) Congestion caused by accident(s) (5) Congestion caused by construction (6) Cause Unclear
<congestion-cause>Natural Congestion</congestion-cause>
This section gives information relating to regulation.
This section describes the regulated target location.
<regulation-place>
<point>
<latitude>Latitude</latitude>
<longitude>Longitude</longitude>
<altitude>Altitude</altitude>
<point-name>Point Name</point-name>
</point>
</regulation-place>
or,
<regulation-place>
<route>
<route-name>Route Name</route-name>
<route-position>Route Position</route-position>
</route>
</regulation-place>
Refer to the notation style in 3.1 Place.
<regulation-place>
<point>
<latitude>41,500000</latitude>
<longitude>142,250000</longitude>
<altitude>15.3</altitude>
<point-name >Nakayama Touge</point-name>
</point>
</regulation-place>
or
<regulation-place>
<route>
<route-name>Hokkaido Longitudinal Expressway</route-name>
<route-position>Chitose/ Chitose IC/Eniwa IC</route-postion>
</route>
</regulation-place>
This section contains the regulation proposed date and time.
<regulation-time>Regulation Proposed Date & Time</regulation-time>
Refer to the notation style in 2.2.1 Date and Time.
<regulation-time>1999-04-01T16:30+09:00</regulation-time>
The regulation class is described.
<regulation-class>Regulation Class</regulation-class>
Regulation class is expressed in characters. Some examples of regulations are listed below.
(1) Traffic Halt (2) Left-Right Turning Regulations (3) Speed Regulations (4) Lane Regulations (5) One Way Traffic Regulations (6) Tire Chain Regulations (7) On-off Ramp Regulations (8) Large Size Motor Vehicle Regulations (9) Transport Regulations (10) Unclear
<regulation-class>Traffic Halt (Winter Traffic Halt)</regulation-class>
This section gives the event causing the regulation.
<regulation-cause>Regulation Cause</regulation-cause>
Regulation cause is expressed in characters. Some examples of causal events are listed below.
(1) Accident (2) Fire (3) Stalled Vehicle (4) Debris / Obstacles in the Road (5) Construction (6) Work (7) Event (8) Weather (9) Disaster (10) Earth Quake Warning (11) Unclear
<regulation-origin>Accident (Physical Injury)</regulation-origin>
This section gives information relating to the direction in which the regulation points or flows.
<regulation-direction>Regulation Direction</regulation-direction>
When the regulation is moving towards a certain direction, note that direction or flow in characters.
<regulation-direction>Moving Southward</regulation-ddirection> or <regulation-direction>Towards Sapporo Kita Interchange</regulation-direction>
This section describes the commencement time or the planned commencement time of the regulation.
<regulation-start>Regulation Commencement Time</regulation-start>
For time notation, refer to the notation style in 2.2.1 Date & Time.
<regulation-start>1999-04-01T16:30+09:00</regulation-start>
This section gives the regulation's planned time of conclusion.
<regulation-end>Regulation Conclusion Time</regulation-end>
If the regulation has a planned conclusion time, note the time. If the conclusion time is unknown or unclear, note "unclear". For time notation, refer to the notation style in 2.2.1 Date & Time.
<regulation-end>1999-04-01T20:30+09:00</regulation-end>
This section gives information related to the traffic volume.
This section describes the location targeted for congestion.
Follow 4.2.1.
This section gives the proposed date and time for traffic volume.
Follow 4.2.2.
This section gives the time unit used during observation of traffic.
<time-unit>Observation Time Unit</time-unit>
Use the observation results from the time unit observation period to determine traffic flow, average speed, average distance between vehicles. To appoint time, refer to the notation style used in the section relating to time period in 2.2.4 Time Length and Period.
<time-unit>PT20M</time-unit>
This section describes the number of vehicles passing through the observation point.
<volume>Traffic Volume</volume>
Traffic volume value is expressed in units of one vehicle passing through the observation point in units of time during the observation time. If it is possible to organize vehicles into classes, notation following the classification can be carried out. Here are examples of general classifications.
Example: Compact Vehicle, Large Vehicle, Total, Unclassifiable
<volume>Large:10,Compact:25,Total: 35</volume>
This section describes the average speed of passing vehicles.
<speed>Average Speed</speed>
The average speed of vehicles passing through the observation period in time units is expressed in units of 1km/hr.
<speed>40</speed>
This section indicates the occupancy rate, given as a unit of volume expressing the condition of traffic density on the road.
<occupancy>Occupancy Rate</occupancy>
The occupancy rate at the observation point is expressed in a percentage.
<occupancy>32</occupancy>
This section gives information relating to travel time measurement.
This section gives the proposed date and time for travel.
Follow 4.2.2.
This section gives point information on the origin which provides travel time.
<origin>Commencement Point</origin>
The proposed point of commencement for travel time is expressed in a characters .
Example: Tomei Expressway 11KP, near Kitahachi Oji bus stop, Tanihara Crossing
<origin>Hokkaido Expressway Osyamanbe Interchange </origin> <origin>Near Muroran Station</origin>
This section gives point information on the destination which provides travel time.
<destination>Destination</destination>
The target position of the travel time measurement is expressed in characters.
Example: Yokohama Interchange, Futaba Service Area Entrance, Itabashi Honcho Crossing
<destination>Hokkaido Expressway Sapporo Nishi Interchange</destination> <destination>Kanayama Parking Area Entrance </destination>
This section gives the route which provides the travel time.
<travel-route>Travel Route</travel-route>
The target route for the travel time measurement is expressed by listing point information. The list divides point information written in characters by a slash [/], and describes in order of starting point => terminal point.
<travel-route>National Route 38/Makubetsucho Honcho/National Route 242</travel-route>
This section gives the travel duration.
<duration>Travel Duration</duration>
The value for the duration of travel time between the travel duration commencement point and the travel duration target point that takes place on the designated date and time is measured in units of 1 minute. To record duration, Refer to the notation style in 2.2.4 Travel Length and Period.
<duration>PT30M</duration>
This section describes the cautions and precautions given to traveler(s).
This section gives the specific information for the travel target place.
<place>
<point>
<latitude>Latitude</latitude>
<longitude>Longitude</longitude>
<altitude>Altitude</altitude>
<point-name>Point Name</point-name>
</point>
</place>
or,
<place>
<route>
<route-name>Route Name</route-name>
<route-position>Route Position</route-position>
</route>
</place>
Refer to the notation style in 2.1 Place.
<place>
<point>
<latitude>41,500000</latitude>
<longitude>142,250000</longitude>
<altitude>15.3</altitude>
<point-name>Nakayama Touge</point-name>
</point>
</place>
or,
<place>
<route>
<route-name>Hokkaido Longitudinal Expressway</route-name>
<route-position>Chitose IC/Eniwa IC</route-postion>
</route>
</place>
This section gives the update time and date for a specific place
<last-update>Last Update Date & Time</last-update>
Refer to the notation style in 3.2.1 Last Update.
<last-update>1999-04-01T16:30+09:00</last-update>
This section describes information that should be dispersed.
<advice spec="Class">Advice</advice>
Advice is expressed in characters. Regulate the classification of advice with the attribute spec.
| Attribute Name | Attribute Value | Value Upon Omission | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| spec | caution, scenery, feature | #REQUIRED | information related to locations that require caution, scenery related information, roadside nature and history, information related to characteristic elements, etc. |
cautions (1) Frequently Occuring Accidents (2) Sudden Bend (3) Sudden Incline (4) Side Wind Caution (5) Fog Caution (6) Snow Storm Caution (7) Frozen Road Surface Caution (8) Animal Crossing Caution (9) Falling Rock Caution (10) Other (characters ) scenery (1) Good Scenery (2) Excellent Scenery (3) Other (characters ) feature Elements such as roadside nature and history, road facilities characteristic of a certain place, etc. are expressed with characters.
<advice spec="attention">Accidents Occur Frequently</attention>
This section gives the URL for the information file related to specific location information.
<info-file href="URL">Information File Name</info-file>
or,
<info-file href="URL" />
List the information file URL in the attribute href. Element titles can be expressed in characters. File attributes are set apart by expansions in the notation.
| Attribute Name | Attribute Value | Value Upon Omission | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| href | CDATA | #REQUIRED | Specify the information file URL. |
For Images <info-file href="http://www.test.com/test001/testimage.jpg" /> For Voice <info-file href="http://www.test.com/test001/testvoice.avi" /> For Text <info-file href="http://www.test.com/test001/testtext.txt" />
This section gives the target period.
<advice-period>Target Period</advice-period>
In recording the period, refer to the notation style in 2.2.4 Time length and period.
<advice-period>--1101/--0331</advice-period> <!-- November 1 to March 31 -->